- India and the Health targets:
- Of the eight MDGs, 3 relate directly to health.
- The first goal was to reduce mortality among children under the age of five; this is only moderately on-track.
- The second goal was to reduce maternal mortality. On this India is off-track.
- India is on-track for the third goal, which was to halt and reverse the spread of HIV/AIDS, and
Showing posts with label Health. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Health. Show all posts
Friday, 2 October 2015
Saturday, 26 September 2015
National Health Profile (NHP) 2015
Predictions on cancer
- 20 per cent jump over the next 5 years, with the increase being higher in women than in men.
- In men - Mouth cancer registering the highest spike despite country wide ban on Gutkha
- In women - Bladder cancer showing the sharpest increase
- Prostate cancer, liver cancer and lung cancer all increasing
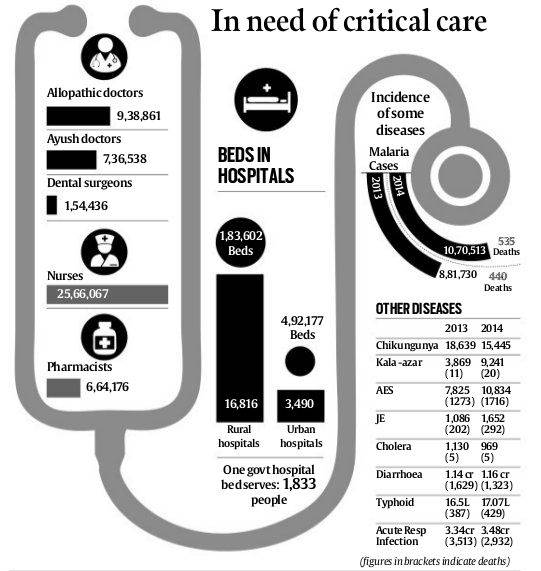
- Number of doctors and others (Approximate)
- Allopathic - 10 million
- AYUSH - 7 Lac
- Dentists - 1.5 Lac
- Nurses - 25 Lac
- Pharmacists - 6 lac
- One govt doctor for 11000 people
- Number of Hospital Beds
- Rural - about 2 lac
- Urban - about 5 lac
- One govt hospital bed serves 2000 people
- Incidence of Disease (Comparison between 2013 and 2014)
- Increased
- Malaria by 25%
- AES - 25%
- Kala Azar Doubled!
- JE - by 50%
- Diarrhoea, Typhoid, acute respiratory Infection - all increased
- Decreased
- Chickungunya
 |
| Image: The Indian Express |
Wednesday, 23 September 2015
Healthcare (Dengue Crisis) in India | Solutions and Examples
"In any free society where terrible wrongs exist, some are guilty; all are responsible.”
- Rabbi Abraham Joshua Heschel
Why in news?
- Many reasons - recent one Dengue deaths in New Delhi
- In most health indicators we are behind South Asian neighbours, other BRICS nations and, for some indicators like child immunisation, sub-Saharan Africa.
- Improper coverage of news - Buried inside a national newspaper on April 12 this year was the heartrending story of a tribal in Odisha who allegedly felt forced to sell his two-month-old son for Rs 700 to buy medicines for his sick wife.
- the state and Central governments,
- municipal corporations,
- private hospitals,
- public health functionaries,
- negligent householders
- careless construction workers who let water stagnate for mosquitos to breed.
- Systemic reforms even after dengue dies seasonally.
- Effective prevention or early and appropriate healthcare
- Mosquito breeding will become even more intense as temperatures rise with climate change.
- Well-coordinated prevention measures that link multiple civic services, government agencies and community organisations;
- Efficient surveillance systems that help in forecasting and monitoring;
- Concerted clinical care strategies that intelligently draw upon the combined resources of public and private providers.
- Regulation, planning and coordination.
- Strengthening of both rural and urban primary health services.
- Whether it is the initial assessment and care of fevers, chronic care of high blood pressure and diabetes or ensuring adherence to tuberculosis treatment, frontline health services can provide most needed healthcare.
- Many patients with viral fevers do not require investigations and treatment at large hospitals — indeed, they run the risk of unnecessary investigations and inappropriate treatment if they do. Triage and referral guidelines will help primary care facilities to steer only the persons who need advanced clinical care to large hospitals.
- Timely and effective risk communication to the public.
- Thailand is a hyper-endemic country for dengue and experienced high numbers of deaths some years ago has now controleld dengue remarkably well. Mehtod-->
- Prevention measures
- Application of a standardised clinical management protocol.
- Tamil Nadu, too, is endemic for dengue but its well-organised public health services are geared to cope with the challenge.
- Mohalla clinics proposed by the Delhi government
- Else, terrible things will continue to happen to innocent children, expectant mothers, poor tribals, disabled persons — and to your family and ours. We will all be responsible when such terrible wrongs happen.
Saturday, 29 August 2015
India is free of Maternal and Newborn Tetanus
What's the news?
- India has successfully eliminated maternal and newborn tetanus (MNT), an infection that at its peak killed some two lakh infants and women in the country
- Describing the achievement as yet another health milestone for India after eradication of polio last year, the PM paid rich tributes to the UPA government’s flagship programme the National Health Mission (NHM). (good example to quote)
- 52% of India’s under-5 mortality is contributed to by deaths of newborns in the first month of life. Under NHM, our approach emphasises a continuum of newborn care both at the community and facility level
Friday, 31 July 2015
Pharma Jan Samadhan Scheme
Why in news?
Launched by Ministry of Chemical and fertilizers
Details;
- for grievance redressal of consumers on drug pricing and availability
- a web-enabled system where consumers can lodge complaints
- web-system run by NPPA
- NPPA will initiate action within 48 hours of the complaint.
- also awareness programs and pharma-literacy initaitives
Thursday, 23 July 2015
Sunday, 19 July 2015
National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) | Drug Price Control Order Para 19
Why in news?
The National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority’s (NPPA) decision last week to expand the number of drugs under price control by a further 39 drugs has no doubt increased scope of price control but the pharmaceutical industry feels the overarching objective of increasing access to medicines is not being adequately addressed.
About NPPA: "Affordable medicine for All"
The National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority’s (NPPA) decision last week to expand the number of drugs under price control by a further 39 drugs has no doubt increased scope of price control but the pharmaceutical industry feels the overarching objective of increasing access to medicines is not being adequately addressed.
About NPPA: "Affordable medicine for All"
Thursday, 16 July 2015
Economic and Health Burden Because of NCDs and Solutions.
- 33% of world poor are in India + 20% of world's disease burden is on India --> More health burden --> Less growth
- Health burden is three fold -
- infectious diseases
- Burden from infectious diseases reduced between 1990 and 2010
- violence/ injuries
- been increasing
- Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), like cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory disease and diabetes.
- 1990-2010 - premature deaths and disability increased due to NCD --> loss of 6% GDP due to total health burden
- NCD -->
- 60% deaths in India,
- 40% of hospital stays
- 35% of outpatient visits.
- Problem is huge! Are we doing enough?
Friday, 10 July 2015
Thursday, 9 July 2015
Tuesday, 30 June 2015
Universal Immunisation | Mission Indradhanush, Rapid Survey of Children (RSOC), Pentavalent Vaccines, NTAGI
Why in news?
What is RSOC?
- The Women and Child Development Ministry, to whom the UN agency submitted the data of the Rapid Survey of Children (RSOC) conducted during 2012-13, has refused to accept it questioning the very basis of the survey.
- Mission Indradhanush, the new scheme launched.
- Several changes in Universal Immunisation Program recently made
What is RSOC?
Tuesday, 23 June 2015
Friday, 19 June 2015
Trans-fats and PHOs
Why in news?
What are trans-fats, PHOs and what are their impacts?
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has announced that it will seek to eliminate majority of partially hydrogenated oils (PHOs) from the country’s food supply by 2018.
- The decision comes after years of lobbying by health advocates and scientists that artificial oils, commonly called “trans fats”, clog arteries and raise the risk of heart disease.
What are trans-fats, PHOs and what are their impacts?
Wednesday, 17 June 2015
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- Established under Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006
- A consolidation of various acts & orders that have hitherto handled food related issues in various Ministries and Departments.
- Created for
- laying down science based standards for articles of food and
- to regulate their manufacture, storage, distribution, sale and import to ensure availability of safe and wholesome food for human consumption.
Establishment
FSSAI Draft Norms for Food Recall
Why in news?
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) came out with the draft norms amid safety concerns over Maggi noodles, which was earlier this month recalled from the market.
Draft Safety and Standards (Food Recall Procedure) Regulations, 2015, has been put up for public comments.
FSSAI has proposed regulations for recall process with the objective to guide the food business operators on how to carry out a recall process.
What is 'Food under recall'?
Friday, 5 June 2015
Fight Against Hunger and State of Food Insecurity Report, 2015
The Millennium Development Goal of halving the proportion of chronically undernourished people in developing countries by 2015 is within reach. But progress must accelerate by the end of this year
Hunger Stats
- Hungry Population —> 800m which is ~10% world Population
- Chronically Hungry - 780m in developing countries
- Decline in hungry people since:
- 2005 - 167m
- 1991 - 200m
- Decline in hungry people since:
- 2005 - 167m
- 1991 - 200m
Friday, 22 May 2015
The story of Maggi Noodles, Monosodium Glutamate (MSG), Lead and Umami
Why in news?
Times of India newspaper recently reported that Samples of Maggi collected from Uttar Pradesh (UP) contained added MSG (Monosodium Glutamate), also known as Ajinomoto, and Lead was multiple times the permissible quantity. So Lucknow's Food Safety and Drug Administration has now started inquiry and written to the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) in New Delhi seeking to cancel the licence for Maggi". Now Maharashtra and Gujarat have also sent the samples for testing.
Times of India newspaper recently reported that Samples of Maggi collected from Uttar Pradesh (UP) contained added MSG (Monosodium Glutamate), also known as Ajinomoto, and Lead was multiple times the permissible quantity. So Lucknow's Food Safety and Drug Administration has now started inquiry and written to the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) in New Delhi seeking to cancel the licence for Maggi". Now Maharashtra and Gujarat have also sent the samples for testing.
What is MSG? Is it harmful? What is Umami? Read ahead to know more.

